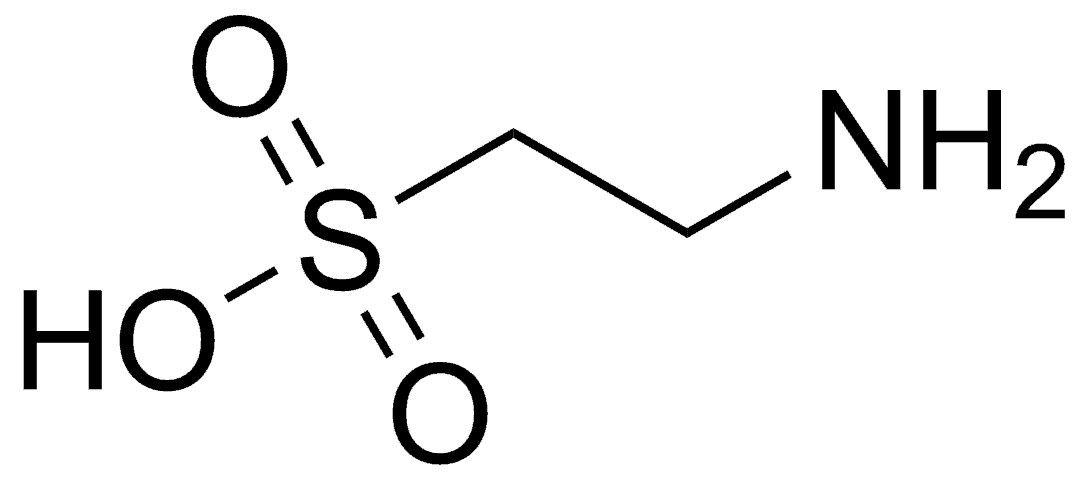
There are ingredients playing an important role in overall health and wellness. One such ingredient ingredient is taurine. It’s classified as sulfonic acid and is thought to play an improtant role in brain health.
What is Taurine?
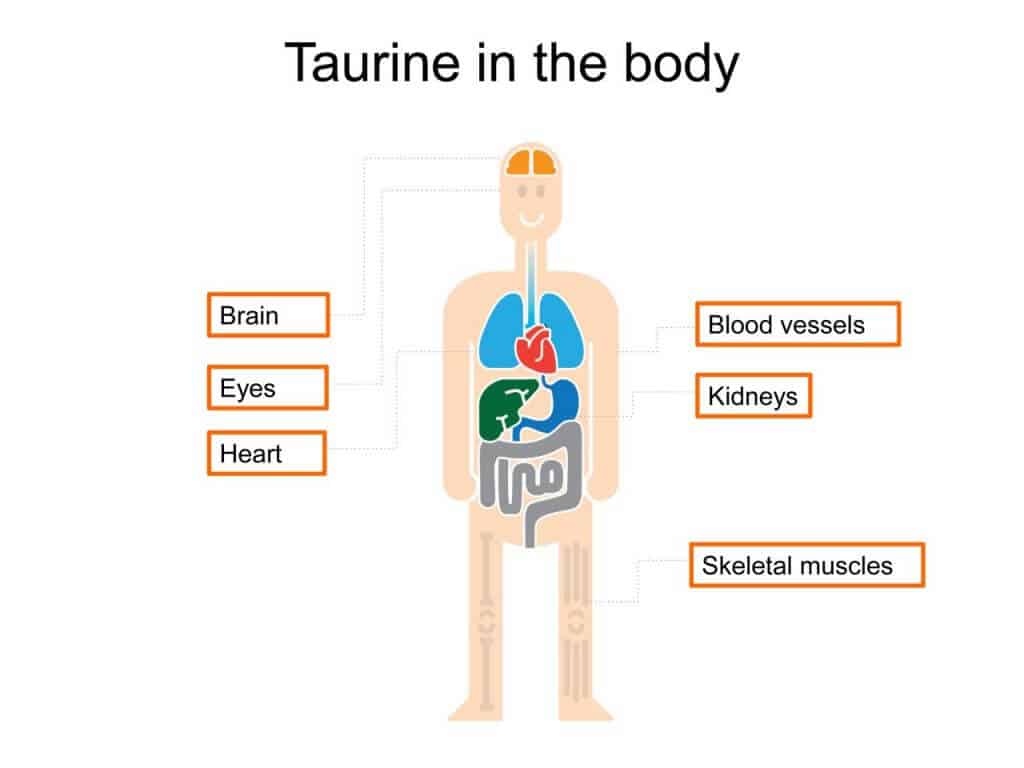
Taurine is an amino acid. For any protein to form, this chemical is required. Although you can find a significant amount of it in blood cells, the heart, retina, and the brain, fish and meat remain as its best sources. It’s not an essential because the body can make a minimal amount of taurine.
When people can’t create taurine for one reason or another, they can obtain it through supplements or a healthy diet. Milk doesn’t provide enough taurine, there may be a need to take a taurine supplement.
Bottom Line: Taurine is an amino acid with potential.
Taurine and Stress
Taking taurine amino acid supplements can help you get in better shape, shed some pounds, and overcome exhaustion. Stress can also be eliminated, and motivation boosted.
As taurine lowers cortisol, it can aid in better sleep, and improved stress management.
It also enhances the performance of an athlete, as well as his/her reaction time.
Taurine fights inflammation, protects the heart, and is a potent nutrient for the brain.
Bottom Line: The supplementation of taurine directly correlates with stress management.
Taurine and Inflammation
Taurine can have powerful effects on blood vessels and the heart.
Plus, they will also have dangerous lipids in lower levels, and lower body mass index.
Bottom Line: Taurine has been found to reduce inflammation and restore the response of arteries to beneficial nitric oxide endothelial.
Taurine and Obesity
Taurine is essential for your overall health because it aids in the fight against obesity. Since every area of your physical body is impacted by cellulite, mainly due to the abdominal fat storage that generates inflammation, taking 3 grams of taurine daily for seven weeks can result in a significant reduction of body weight, as research confirms.
Various studies on animals support the lipid-lowering and anti-obese capacities of taurine when combined with other products and also when it was used alone, as well as taurine’s ability to improve tolerance to glucose.
Research done on animals has resulted in the decline of plasma taurine levels, creating vicious obesity cycles.
Mice with diet-induced obesity and genetic obesity were observed. In a similar study, supplementation with taurine caused the cycle to become interrupted, which helped in preventing the consequences of obesity.
Bottom Line: Taurine may help with obesity.

Taurine Supplements
With so much energy these days focused on investigating new compounds that could help longevity, many decades-old venerable ones tend to be forgotten in the sidelines. Taurine is one example.
A 2012 study posted on Life Extension stated:
“Considering its broad distribution, its many cytoprotective attributes, and its functional significance in cell development, nutrition, and survival, taurine is undoubtedly one of the essential substances in the body.”
Of course, producing taurine might be something your body can do. However, for optimal results, obtaining it from supplementation and your diet is still necessary.
Bottom Line: Supplements containing taurine are essential for every human being seeking to improve their health.
Taurine and Longevity
The Japanese have the highest rates of life expectancy in the world. Most people over the age of a hundred can be found on Longevity Island. A common connection discovered in the population there was that it had a high intake of taurine amino acid in diets.
Because there is such a strong link between long life and taurine, the Japanese refer to this amino acid as the “Japanese longevity nutrition factor.”
In research done on animals, it was discovered it protected against heart failure, reducing the rates of mortality by up to 80% perfect.
Bottom Line: Taurine can lead to longevity. It also promotes immune modulation, hearing function, electrolyte balance, insulin sensitivity, and cardiovascular health. There were such extensive, broad benefits that at times, scientists called taurine a “molecule wonder.”

Increased Taurine Levels
Typically, taurine can be found in most fit bodies. However, adequate amounts have not been discerned in vegan or vegetarian diets.
Also, aging bodies are usually unable to produce optimum amounts of taurine, thus emphasizing the significance of supplementation.
Bottom Line: This nutrient is low-cost and can help with neurologic health, metabolic health and cardiovascular health.
Taurine and the Nervous System
Let’s face it: less stress is something every individual needs. Taurine can assist in such a phenomenon, as it facilitates the GABA neurotransmitter that calms the nervous system, according to a study published by the Journal of Biomedical Science. When the levels of GABA are raised, taurine improves stress management, thus shielding you from the spikes of adrenaline and cortisol.
According to a study published by Amino Acids, your nerves tend to over-respond to stressful situations when taurine is on the lower end of the spectrum. A nervous system consistently excited will mean high cortisol all the time, increasing body fat.
Bottom Line: If losing fat is something you have experienced, you know that your body tends to shed fat more efficiently when it is calm compared to when it is agitated.
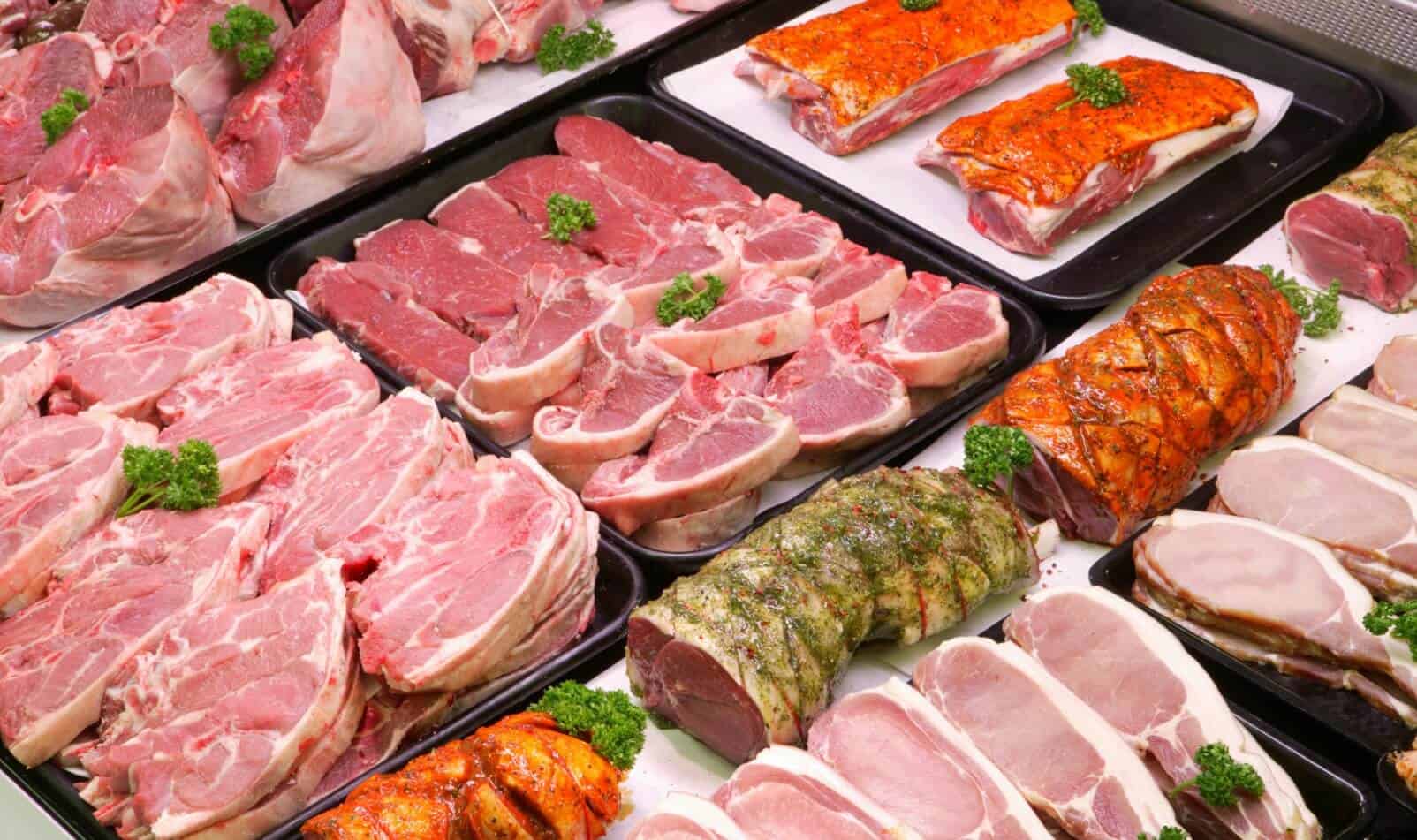

Taurine Sources
According to Livestrong, meat and seafood naturally contain taurine. In most societies, however, the consumed amount is not as high as it could be. Taurine is not as abundant in plants.
Typically, non-vegetarians consume between forty-three to seventy-six milligrams of taurine daily.
Here is a list of food groups with ample amounts:
- Raw meat
- Brewer’s yeast
- Krill
- Seaweed
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Dark chicken meat
- Lamb
- Beef
Bottom Line: Vegetarians tend to have lower levels of taurine in their blood.
What Users Are Saying
“I started using this as part of my pre-workout supplements. After using, I have noticed that my endurance has increased and I have been able to do more reps, especially in the bench press. I would highly advise anyone to take this if they do not include taurine in their pre-workout.”
“I bought this product because I saw so much positive feedback and reviews. However, my experience with it was not that enchanting. I feel no big different after taking it.”
“It doesn’t seem to do anything.”
Bottom Line on Taurine
There is a good reason that the longest living populations in the world applaud taurine as their superpower. High intakes could indeed be the factor that improves longevity in human beings.
With the evidence of epidemiology contributing to the long lives of people, this amino sulfonic acid belongs on the list of supplements can for maintaining optimum health. However, for optimal weight, you may want to consider a comprehensive program instead of supplementation.
Noom is one of the best programs we have ever seen. This weight-loss app works by providing its users with an extensive food logging database, nutritional lessons, exercise tracking, and personal meal plans. Plus, the program is backed by multiple published clinical studies – something that most weight-loss products can’t claim.
Right now, Noom is offering a free trial offer to all readers. It’s only available for a limited time though, so make sure to give it a try while the offer lasts!
Taurine – Benefits, Side Effects and Usage Questions & Answers
Taurine is a nutrient, specifically an amino acid, that can be obtained from fish, meat, and human breast milk. You can take it as a pill as well. Taurine is believed to be an antioxidant, and it is essential for brain function and blood osmosis.
Taurine is important for the health of the brain, heart, eyes, and blood cells. It is also a necessary component of protein, known as an amino acid or amino sulfonic acid.
Babies and young children should take about 27 to 58 milligrams per kilogram that they weigh. A kid who weighs nine kilograms, for example, would take between 243 and 522 milligrams per day.
Taurine is a nutrient whose name is derived from the Latin word for bull. That’s because people used to get taurine from the bile or seminal fluid of cattle. Taurine can also be obtained from breast milk, intestines, fish and meat.
Synthetic taurine is made via a chemical reaction. There are two ways of going about this; you can combine sodium bisulfite and ethylene oxide to yield isethionic acid (a precursor to taurine), or you can combine sulfurous acid and aziridine to yield taurine.
Free form taurine exists inside neurons, blood cells and muscle cells. Taurine is like an amino acid, but it is not a true amino acid because it is not a component of proteins.
Your body needs taurine to synthesize GABA. This neurotransmitter, along with theanine, can be used to treat anxiety.
Taurine is already present naturally in the human body, which synthesizes it from a molecule called cysteine. It used to be extracted from the bile and seminal fluid of cattle for use as a supplement, and now it is usually synthesized in a lab. It is perfectly safe, though you can get plenty of it just from eating a healthy and nutritious diet.
Taurine imitates neurotransmitters by electrically stimulating neurons. It can increase brain activity and communication in this way.
Taurine deficiency can cause a wide range of health problems, including digestive dysfunction, weakened heart muscles, and central retinal degeneration.
No, taurine is not as strong as caffeine. Taurine can provide a mild energy boost, but it doesn’t have the same level of intensity as caffeine. Caffeine provides an immediate jolt to get you going, while taurine works more slowly and steadily to increase alertness over time.
Taurine – Benefits, Side Effects and Usage Questions & Answers
Taurine is a nutrient, specifically an amino acid, that can be obtained from fish, meat, and human breast milk. You can take it as a pill as well. Taurine is believed to be an antioxidant, and it is essential for brain function and blood osmosis.
Taurine is important for the health of the brain, heart, eyes, and blood cells. It is also a necessary component of protein, known as an amino acid or amino sulfonic acid.
Babies and young children should take about 27 to 58 milligrams per kilogram that they weigh. A kid who weighs nine kilograms, for example, would take between 243 and 522 milligrams per day.
Taurine is a nutrient whose name is derived from the Latin word for bull. That’s because people used to get taurine from the bile or seminal fluid of cattle. Taurine can also be obtained from breast milk, intestines, fish and meat.
Synthetic taurine is made via a chemical reaction. There are two ways of going about this; you can combine sodium bisulfite and ethylene oxide to yield isethionic acid (a precursor to taurine), or you can combine sulfurous acid and aziridine to yield taurine.
Free form taurine exists inside neurons, blood cells and muscle cells. Taurine is like an amino acid, but it is not a true amino acid because it is not a component of proteins.
Your body needs taurine to synthesize GABA. This neurotransmitter, along with theanine, can be used to treat anxiety.
Taurine is already present naturally in the human body, which synthesizes it from a molecule called cysteine. It used to be extracted from the bile and seminal fluid of cattle for use as a supplement, and now it is usually synthesized in a lab. It is perfectly safe, though you can get plenty of it just from eating a healthy and nutritious diet.
Taurine imitates neurotransmitters by electrically stimulating neurons. It can increase brain activity and communication in this way.
Taurine deficiency can cause a wide range of health problems, including digestive dysfunction, weakened heart muscles, and central retinal degeneration.
No, taurine is not as strong as caffeine. Taurine can provide a mild energy boost, but it doesn’t have the same level of intensity as caffeine. Caffeine provides an immediate jolt to get you going, while taurine works more slowly and steadily to increase alertness over time.
Article Sources
- https://www.lifeextension.com/magazine/2013/6/the-forgotten-longevity-benefits-of-taurine/page-01
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2994408/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22903433
- https://www.livestrong.com/article/305394-how-many-calories-are-in-dungeness-crab/
- https://www.amazon.com/NOW-Taurine-1000-100-Capsules/product-reviews/B0019LRYD0/ref=cm_cr_dp_d_hist_5?ie=UTF8&filterByStar=five_star&reviewerType=avp_only_reviews#reviews-filter-bar
- https://www.amazon.com/NOW-Taurine-1000-100-Capsules/product-reviews/B0019LRYD0/ref=cm_cr_arp_d_viewopt_sr?ie=UTF8&filterByStar=three_star&reviewerType=avp_only_reviews&pageNumber=1#reviews-filter-bar
- https://www.amazon.com/NOW-Taurine-1000-100-Capsules/product-reviews/B0019LRYD0/ref=cm_cr_arp_d_hist_2?ie=UTF8&filterByStar=two_star&reviewerType=avp_only_reviews&pageNumber=1#reviews-filter-bar
- https://noom.8utb.net/c/1720052/500038/8591
- https://noom.8utb.net/c/1720052/500038/8591
Partner with Us!
Looking to promote your weight-loss products or services?
Our platform reaches a dedicated audience actively seeking the best solutions. Contact us to explore advertising opportunities and grow your brand with us.
Get in Touch